A research revealed within the journal PNAS reveals that the intestine microbiome stabilizes the synchronization between intestine and mind circadian rhythms.
 Research: The microbiome stabilizes circadian rhythms within the intestine. Picture Credit score: Vovantarakan / Shutterstock
Research: The microbiome stabilizes circadian rhythms within the intestine. Picture Credit score: Vovantarakan / Shutterstock
Background
The intestine microbiome is a group of microorganisms that reside within the human/animal digestive tract. It performs an important position in regulating varied physiological processes, together with metabolism, immune response, and neurological capabilities.
Though the intestine microbiome stays secure in the long run, weight loss plan can induce transient adjustments in its composition. Equally, the intestine microbiome reveals rhythmic variations in composition and localization all through a day-night cycle.
Within the present research, scientists have explored the interaction between the intestine microbiome, time-restricted feeding sample, and circadian rhythms within the Drosophila (frequent fruit fly) intestine.
Circadian regulation of intestine microbiome
Drosophila with a limiteless meals provide (advert libitum) have been used to check whether or not the intestine microbiome composition and variety change over the course of the day-night cycle. The findings revealed no circadian biking of the intestine microbiota in wild-type flies and in flies missing a circadian clock gene.
The wild-type flies subjected to rhythmic feeding patterns at particular time factors additionally revealed no circadian variations in intestine microbiota composition and variety. Nonetheless, in flies missing a circadian clock gene, circadian clocks have been discovered to intervene with the impact of time-restricted feeding patterns on the intestine microbiome.
Impression of time-restricted feeding on circadian transcriptome
The evaluation of circadian gene expression was carried out within the research utilizing flies with and with no microbiome. The findings revealed that each time-restricted feeding and microbiome loss considerably affect the intestine’s circadian transcriptome.
Host genes encoding metabolic proteins confirmed elevated biking in flies with no microbiome (sterile). In distinction, genes related to growth and differentiation confirmed decreased biking.
In flies maintained beneath time-restricted feeding situations (meals supplied at particular time factors), lack of biking expression was noticed for genes related to oxidative phosphorylation and power metabolism.
An induction in biking gene expression was noticed beneath time-restricted feeding situations. Altered actions of transcription components have been discovered to be accountable for the worldwide adjustments in biking expression. Just like time-restricted feeding, lack of microbiome was discovered to affect biking gene expression.
The impact of time-restricted feeding on biking gene expression gave the impression to be mediated by elevated histone acetylation. The findings revealed that restricted feeding situations set off strong rhythms of histone acetylation and that many genes affected by these situations are aware of histone acetylation.
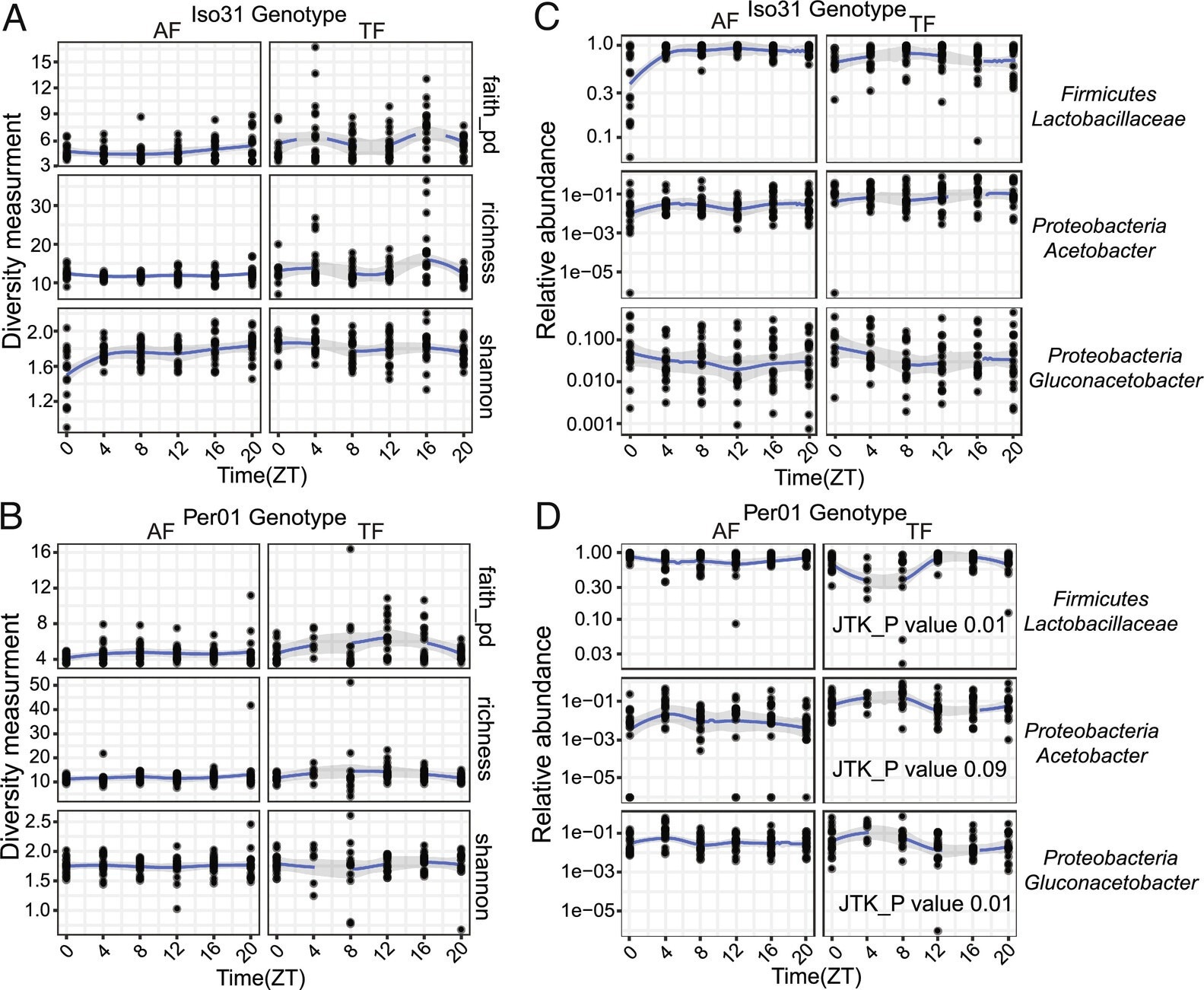 The Drosophila intestinal microbiome is essentially secure over a each day cycle. (A and B) Microbiome range doesn’t present diurnal oscillations in wild kind Iso31 or clock mutant per01 fly guts beneath advert−lib (AF) or TF situations. JTK_cycle was used to evaluate rhythmicity. (C and D) Particular bacterial species cycle beneath TF situations, however solely in per01. JTK_cycle values are proven.
The Drosophila intestinal microbiome is essentially secure over a each day cycle. (A and B) Microbiome range doesn’t present diurnal oscillations in wild kind Iso31 or clock mutant per01 fly guts beneath advert−lib (AF) or TF situations. JTK_cycle was used to evaluate rhythmicity. (C and D) Particular bacterial species cycle beneath TF situations, however solely in per01. JTK_cycle values are proven.
Purposeful affect of time-restricted feeding and microbiome
Flies maintained with time-restricted feeding have been subjected to totally different stressors (hunger, micro organism injection, and warmth shock) to find out the affect of restricted feeding on well being and health.
The findings revealed that restricted feeding reduces the survival of flies in annoying situations. In different phrases, restricted feeding will increase the sensitivity of flies to stressors, regardless of having helpful metabolic results.
The practical affect of the microbiome was decided utilizing the circadian part shift paradigm (altered course of the day-night cycle). For the experiments, flies with and with out microbiomes have been used.
The findings revealed that the microbiome’s presence will increase circadian clock gene biking in flies’ brains. General, it was noticed that sterile flies reset extra quickly with shifts within the day-night cycle in comparison with flies with a microbiome.
In different phrases, the intestine microbiome modulates the intestine clock response to alterations within the day-night cycle, facilitating the synchronization between intestine and mind circadian rhythms.
Research significance
The research reveals that the intestine microbiome in flies doesn’t cycle. Nonetheless, it regulates circadian rhythms of gene expression within the intestine and prevents speedy fluctuations in response to totally different environmental situations.
Because the scientists within the journal talked about, “these findings have essential implications for frequent conditions within the trendy world.”
Supply:
Zhang Y. 2023. The microbiome stabilizes circadian rhythms within the intestine. PNAS, https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2217532120
