A latest examine on Swedish adults explored the prevalence of psychological well being signs earlier than and after immunization with coronavirus illness 2019 (COVID-19) vaccines. The examine is revealed within the journal PLOS ONE.
 Research: Quick-term enchancment of psychological well being after a COVID-19 vaccination. Picture Credit score: eamesBot / Shutterstock
Research: Quick-term enchancment of psychological well being after a COVID-19 vaccination. Picture Credit score: eamesBot / Shutterstock
Background
The COVID-19 pandemic attributable to extreme acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has considerably negatively impacted the psychological well being standing of each contaminated and non-infected people globally. An elevated danger of creating psychiatric issues, together with melancholy and anxiousness, has been noticed amongst severely contaminated people, in all probability due to SARS-CoV-2-induced neuroinflammation.
Other than direct an infection, pandemic-related social restrictions in addition to the worry of contracting an infection, have prompted a deterioration in psychological well being amongst non-infected people.
COVID-19 vaccines have led to a big discount in circumstances and severity of the illness worldwide. Nonetheless, the influence of vaccination on psychological well being and wellbeing stays poorly understood.
Within the present examine, scientists have decided the short-term adjustments in psychological well being signs amongst people immunized with COVID-19 vaccines.
Research design
The examine was carried out on 7,925 Swedish adults. Self-reported COVID-19 vaccination standing was collected from the individuals between July and October 2021. Self-reported depressive and anxiousness signs had been collected from the individuals between December 2020 and October 2021.
The prevalence of psychological well being signs was estimated one month earlier than and after the primary vaccination and in some circumstances, one month after the second vaccination. The depressive and anxiousness signs had been estimated utilizing the Affected person Well being Questionnaire and the Generalized Anxiousness Dysfunction, respectively. The individuals reporting no vaccination or selected to not report vaccination standing had been thought-about unvaccinated.
Necessary observations
Amongst enrolled individuals, 64% acquired two vaccine doses, 24.9% acquired a single dose, 3.8% didn’t obtain any vaccination, and seven.1% selected to not report vaccination standing.
A decrease prevalence of depressive and anxiousness signs was noticed amongst vaccinated individuals, particularly after the second vaccination, in comparison with unvaccinated people.
Amongst individuals with two-dose vaccination, a discount in psychological well being signs was noticed one month after the primary and second vaccination. The same development was noticed amongst individuals who acquired solely a single dose of COVID-19 vaccines.
No vital discount in depressive or anxiousness signs was noticed amongst unvaccinated individuals over your complete examine interval. Nonetheless, after 4 months, the baseline estimates confirmed a discount within the prevalence of depressive signs when in comparison with these obtained at baseline.
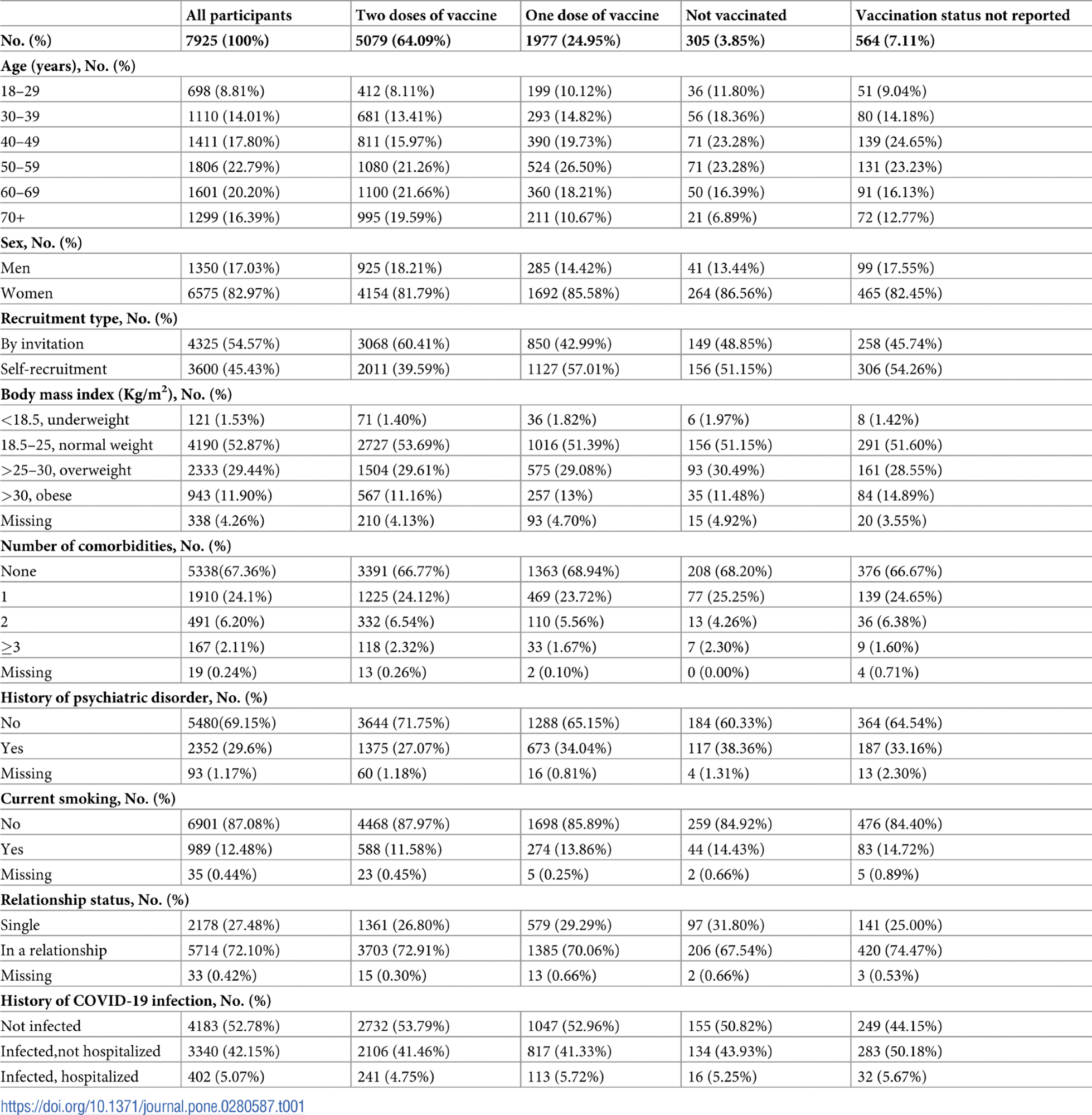 Baseline traits of the examine individuals by vaccination standing.
Baseline traits of the examine individuals by vaccination standing.
Research significance
The examine demonstrates a short-term enchancment within the prevalence of depressive and anxiousness signs after COVID-19 vaccination amongst numerous Swedish adults. The development turns into extra distinguished after the second vaccination, regardless of age, intercourse, physique mass index, relationship standing, smoking behavior, presence of comorbidities, historical past of psychiatric issues, and SARS-CoV-2 an infection standing.
As talked about by the scientists, the examine could undergo from choice bias because the individuals had been recruited from ongoing research or social media campaigns. Thus, the individuals might need completely different statuses concerning COVID-19 vaccination and psychological well being outcomes.
Furthermore, the examine analyzed self-reported data on vaccination and psychological well being standing, which might result in misclassification of publicity and outcomes. Socioeconomic variations between individuals weren’t addressed within the examine. Nonetheless, such variations can affect particular person willingness to COVID-19 vaccination in addition to psychological issues.
Regardless of these limitations, the examine highlights that COVID-19 vaccines will not be solely efficient in lowering illness severity but additionally efficient in bettering psychological well being and wellbeing. The examine helps the initiation of outreach campaigns concentrating on vaccine-hesitant people for the general betterment of the psychological well being standing of the final inhabitants.
